nixos nfs
I migrated from FreeBSD to NixOS for my nas. Apparently I never tested/used NFS on the new OS. When I went to mount my music share from my OpenBSD client I received the following error.
NFS Portmap: RPC: Program not registered
I followed this guide to add NFS to the NixOS config.
That partially worked. I could use the local client in the example to connect and an Arch Linux client could connect. But my OpenBSD client would not connect.
After some (ok a lot) of searching I stumbled upon this guide, which suggested to run the below rpcinfo commands.
rpcinfo -t hostname mountd
rpcinfo -u hostname mountd
rpcinfo -t hostname nfs
rpcinfo -u hostname nfs
When I got to this one it became obvious what was really going on.
rpcinfo -u nas nfs
rpcinfo: RPC: Program not registered
program 100003 is not available
It turns out that OpenBSD defaults to using UDP for NFS and Linux defaults to TCP. When I had ran my rpcinfo command I didn’t notice that there was a UDP entry missing for the NFS service.
rpcinfo -p nas
program vers proto port
100000 4 tcp 111 portmapper
100000 3 tcp 111 portmapper
100000 2 tcp 111 portmapper
100000 4 udp 111 portmapper
100000 3 udp 111 portmapper
100000 2 udp 111 portmapper
100024 1 udp 4000 status
100024 1 tcp 4000 status
100005 1 udp 4002 mountd
100005 1 tcp 4002 mountd
100005 2 udp 4002 mountd
100005 2 tcp 4002 mountd
100005 3 udp 4002 mountd
100005 3 tcp 4002 mountd
100003 3 tcp 2049 nfs
100003 4 tcp 2049 nfs
100227 3 tcp 2049
100021 1 udp 4001 nlockmgr
100021 3 udp 4001 nlockmgr
100021 4 udp 4001 nlockmgr
100021 1 tcp 4001 nlockmgr
100021 3 tcp 4001 nlockmgr
100021 4 tcp 4001 nlockmgr
showmount -e nas
Exports list on nas:
export 192.168.88.0/24
export/music 192.168.88.0/24
I tried mount_nfs with the -T option to specify using TCP and it worked!
mount_nfs -T nas:/export/music /mnt/nas-media
I then hunted around for the flag for NixOS to add a UDP service for NFS. You need to add udp=y. The below is the NFS config for my NixOS.
services = {
nfs = {
server.enable = true;
server.exports = ''
/export 192.168.88.0/24(rw,fsid=0,no_subtree_check)
/export/music 192.168.88.0/24(rw,nohide,insecure,no_subtree_check)
'';
# for nvsv3
# fixed rpc.statd port; for firewall
server.statdPort = 4000;
server.lockdPort = 4001;
server.mountdPort = 4002;
server.extraNfsdConfig = ''udp=y'';
}:
}:
After upgrading to nixos 24.05 services.nfs.server.extraNfsConfig was deprecated. You now use services.nfs.settings. That config would like the below.
services = {
nfs = {
server.enable = true;
server.exports = ''
/export 192.168.88.0/24(rw,fsid=0,no_subtree_check)
/export/music 192.168.88.0/24(rw,nohide,insecure,no_subtree_check)
'';
# for nvsv3
# fixed rpc.statd port; for firewall
server.statdPort = 4000;
server.lockdPort = 4001;
server.mountdPort = 4002;
settings = {
nfsd.udp = true;
};
}:
}:
# Open ports in the firewall.
networking.firewall.enable = true;
networking.firewall.allowedTCPPorts = [ 111 2049 4000 4001 4002 20048 ];
networking.firewall.allowedUDPPorts = [ 111 2049 4000 4001 4002 20048 ];
Now rpcinfo shows:
rpcinfo -p nas
program vers proto port
100000 4 tcp 111 portmapper
100000 3 tcp 111 portmapper
100000 2 tcp 111 portmapper
100000 4 udp 111 portmapper
100000 3 udp 111 portmapper
100000 2 udp 111 portmapper
100005 1 udp 4002 mountd
100005 1 tcp 4002 mountd
100005 2 udp 4002 mountd
100005 2 tcp 4002 mountd
100005 3 udp 4002 mountd
100005 3 tcp 4002 mountd
100024 1 udp 4000 status
100024 1 tcp 4000 status
100003 3 tcp 2049 nfs
100003 4 tcp 2049 nfs
100227 3 tcp 2049
100003 3 udp 2049 nfs
100227 3 udp 2049
100021 1 udp 4001 nlockmgr
100021 3 udp 4001 nlockmgr
100021 4 udp 4001 nlockmgr
100021 1 tcp 4001 nlockmgr
100021 3 tcp 4001 nlockmgr
100021 4 tcp 4001 nlockmgr
Also NixOS supports NFS versions 3 through 4.2 and OpenBSD supports versions 2 and 3. However both OSs do successfully negotiate to use version 3.
Ikea Kallax
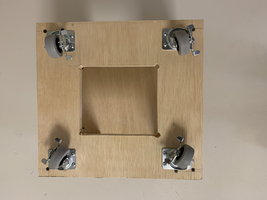
Made a base for my Ikea Kallax shelf so that:
1) If my basement has a minor flood the press board won’t get wet.
2) It can be moved around.
3) It can be raised off of the floor.
One of the big questions was how to fasten the base to the shelf. Was there any substance in the bottom shelf that the screws could fasten to and would it hold to the base. Ie or would the screws just pull out?
You can click on any of the pics for a larger image, that you can then enlarge.
Pics of custom base:
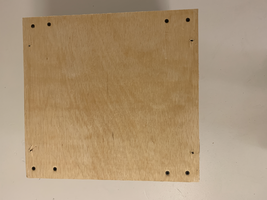
Pics of the partially finished base:
The access hole in the bottom of the base is so I can reach my hand in to screw the base on to the shelf.
Pics of the finished base:
Pics of how I screwed the base to the shelf:
Note the shelf is upside down and the base with the wheels up will be placed on the shelf.
There is solid material in the corners of the shelf for the screws to assemble the shelf to the sidewalls, so the screws won’t pull through the shelf. I angled the screw towards the corners.
Pic of shelf on the unfinished base:
Pics of the finished shelf and base!:
And yes the concrete floor is not very level. I ended up putting levelers in the corners.
I really didn’t need this size bolt for strength. But if you wanted ~4.5 inches, that is the size they had.
I built one for a 1x4, 2x4, and 3x4 Ikea shelf. So the base dimensions will depend on what kind of shelf you pick.
The frame was built with scrap wood. The exterior was primed trim board. I didn’t have any trim board so you can choose any style trim you want.
I tried to balance the height of the trim board to minimize the number of boards.
digital picture frame
I have wanted a digital picture frame for a while now. However I have not wanted to spend the money for a store bought product and thought building one sounded rather complicated.
After thinking about it for a while I decided using a 15"ish monitor and a Raspberry Pi zero W would greatly simplify the project. It would really just turn it into a few scripts and hooking up a monitor with the pi. If I had tried to drive an LCD panel it would have been a lot more work.
I found an HDMI monitor on FB Buy Nothing. I had a rPi hanging around. I just had to buy a few cables.
FEH does all of the hard work. It can randomize the pictures in a directory tree, delay how long to show them, go full screen, etc. The only thing that made it a little complicated was feh has a memory leak. It took a bit to discover that. Once I had figured that out I just added a loop around feh to restart it after each crash.
FEH memory leak:
https://github.com/derf/feh/issues/553
Script to run feh. Just point to it from crontab. I stored my pictures on my NAS, and just update them once a month.
cat play.sh
#!/bin/sh
while true
do
feh --fullscreen --auto-zoom --randomize --hide-pointer --recursive --slideshow-delay 20 /mnt/pictures/kids_pics/pics
echo "sleeping..."
sleep 60
done
nixos hostapd
I am building a router with PC Engines APU board. I wanted to use NIXOS with hostapd.
I was not able to find complete documentation for how to configure it for N and AC in the US.
The ath10k also needs an updated regulatory database.
I needed two changes to get the regulatory database.
In my hardware-configuration.nix file I added:
hardware = {
enableAllFirmware = true;
enableRedistributableFirmware = true;
# NOTE: When 21.11 lands, swap for:
# wirelessRegulatoryDatabase = true;
firmware = [ pkgs.wireless-regdb ];
};
In my configuration.nix file my redacted hostapd entry looks like:
services.hostapd = {
enable = true;
interface = "wlp5s0";
ssid = "ssid";
wpaPassphrase = (builtins.readFile "/etc/nixos/wpa_passphrase.txt");
hwMode = "a";
channel = 0;
countryCode = "US";
extraConfig =
''
# turn off dfs (ie outdoor ir/radar detection)
ieee80211h=0
ieee80211n=1
wmm_enabled=1
ht_capab=[HT40+][HT40-][SHORT-GI-20][SHORT-GI-40][DSSS_CK-40][MAX-AMSDU-7935]
ieee80211ac=1
vht_oper_chwidth=1
vht_capab=[SHORT-GI-80][TX-STBC-2BY1][RX-STBC-1][MAX-MPDU-11454]
'';
}
This config option was also added, but it is not clear if it was necessary as my hostapd configs were not correct when this was added. It took many (15'ish) hours to recompile nixos.
networking.wireless.athUserRegulatoryDomain = true;
iw dev
phy#0
Interface wlp5s0
ifindex 6
wdev 0x1
addr 04:f0:21:b5:a0:2b
ssid rivendell
type AP
channel 40 (5200 MHz), width: 80 MHz, center1: 5210 MHz
txpower 23.00 dBm
multicast TXQ:
qsz-byt qsz-pkt flows drops marks overlmt hashcol tx-bytes tx-packets
0 0 15938 0 0 0 15 4529069 15942
iw list
Wiphy phy0
wiphy index: 0
max # scan SSIDs: 16
max scan IEs length: 195 bytes
max # sched scan SSIDs: 0
max # match sets: 0
Retry short limit: 7
Retry long limit: 4
Coverage class: 0 (up to 0m)
Device supports RSN-IBSS.
Device supports AP-side u-APSD.
Supported Ciphers:
* WEP40 (00-0f-ac:1)
* WEP104 (00-0f-ac:5)
* TKIP (00-0f-ac:2)
* CCMP-128 (00-0f-ac:4)
* CMAC (00-0f-ac:6)
* CMAC-256 (00-0f-ac:13)
* GMAC-128 (00-0f-ac:11)
* GMAC-256 (00-0f-ac:12)
Available Antennas: TX 0x3 RX 0x3
Configured Antennas: TX 0x3 RX 0x3
Supported interface modes:
* managed
* AP
* AP/VLAN
* monitor
Band 1:
Capabilities: 0x19ef
RX LDPC
HT20/HT40
SM Power Save disabled
RX HT20 SGI
RX HT40 SGI
TX STBC
RX STBC 1-stream
Max AMSDU length: 7935 bytes
DSSS/CCK HT40
Maximum RX AMPDU length 65535 bytes (exponent: 0x003)
Minimum RX AMPDU time spacing: 8 usec (0x06)
HT TX/RX MCS rate indexes supported: 0-15
Bitrates (non-HT):
* 1.0 Mbps
* 2.0 Mbps (short preamble supported)
* 5.5 Mbps (short preamble supported)
* 11.0 Mbps (short preamble supported)
* 6.0 Mbps
* 9.0 Mbps
* 12.0 Mbps
* 18.0 Mbps
* 24.0 Mbps
* 36.0 Mbps
* 48.0 Mbps
* 54.0 Mbps
Frequencies:
* 2412 MHz [1] (20.0 dBm)
* 2417 MHz [2] (20.0 dBm)
* 2422 MHz [3] (20.0 dBm)
* 2427 MHz [4] (20.0 dBm)
* 2432 MHz [5] (20.0 dBm)
* 2437 MHz [6] (20.0 dBm)
* 2442 MHz [7] (20.0 dBm)
* 2447 MHz [8] (20.0 dBm)
* 2452 MHz [9] (20.0 dBm)
* 2457 MHz [10] (20.0 dBm)
* 2462 MHz [11] (20.0 dBm)
* 2467 MHz [12] (20.0 dBm)
* 2472 MHz [13] (20.0 dBm)
* 2484 MHz [14] (disabled)
Band 2:
Capabilities: 0x19ef
RX LDPC
HT20/HT40
SM Power Save disabled
RX HT20 SGI
RX HT40 SGI
TX STBC
RX STBC 1-stream
Max AMSDU length: 7935 bytes
DSSS/CCK HT40
Maximum RX AMPDU length 65535 bytes (exponent: 0x003)
Minimum RX AMPDU time spacing: 8 usec (0x06)
HT TX/RX MCS rate indexes supported: 0-15
VHT Capabilities (0x338001b2):
Max MPDU length: 11454
Supported Channel Width: neither 160 nor 80+80
RX LDPC
short GI (80 MHz)
TX STBC
RX antenna pattern consistency
TX antenna pattern consistency
VHT RX MCS set:
1 streams: MCS 0-9
2 streams: MCS 0-9
3 streams: not supported
4 streams: not supported
5 streams: not supported
6 streams: not supported
7 streams: not supported
8 streams: not supported
VHT RX highest supported: 0 Mbps
VHT TX MCS set:
1 streams: MCS 0-9
2 streams: MCS 0-9
3 streams: not supported
4 streams: not supported
5 streams: not supported
6 streams: not supported
7 streams: not supported
8 streams: not supported
VHT TX highest supported: 0 Mbps
VHT extended NSS: not supported
Bitrates (non-HT):
* 6.0 Mbps
* 9.0 Mbps
* 12.0 Mbps
* 18.0 Mbps
* 24.0 Mbps
* 36.0 Mbps
* 48.0 Mbps
* 54.0 Mbps
Frequencies:
* 5180 MHz [36] (23.0 dBm)
* 5200 MHz [40] (23.0 dBm)
* 5220 MHz [44] (23.0 dBm)
* 5240 MHz [48] (23.0 dBm)
* 5260 MHz [52] (20.0 dBm) (radar detection)
* 5280 MHz [56] (20.0 dBm) (radar detection)
* 5300 MHz [60] (20.0 dBm) (radar detection)
* 5320 MHz [64] (20.0 dBm) (radar detection)
* 5500 MHz [100] (26.0 dBm) (radar detection)
* 5520 MHz [104] (26.0 dBm) (radar detection)
* 5540 MHz [108] (26.0 dBm) (radar detection)
* 5560 MHz [112] (26.0 dBm) (radar detection)
* 5580 MHz [116] (26.0 dBm) (radar detection)
* 5600 MHz [120] (26.0 dBm) (radar detection)
* 5620 MHz [124] (26.0 dBm) (radar detection)
* 5640 MHz [128] (26.0 dBm) (radar detection)
* 5660 MHz [132] (26.0 dBm) (radar detection)
* 5680 MHz [136] (26.0 dBm) (radar detection)
* 5700 MHz [140] (26.0 dBm) (radar detection)
* 5720 MHz [144] (13.0 dBm) (radar detection)
* 5745 MHz [149] (13.0 dBm)
* 5765 MHz [153] (13.0 dBm)
* 5785 MHz [157] (13.0 dBm)
* 5805 MHz [161] (13.0 dBm)
* 5825 MHz [165] (13.0 dBm)
* 5845 MHz [169] (13.0 dBm)
* 5865 MHz [173] (13.0 dBm)
Supported commands:
* new_interface
* set_interface
* new_key
* start_ap
* new_station
* set_bss
* authenticate
* associate
* deauthenticate
* disassociate
* join_ibss
* remain_on_channel
* set_tx_bitrate_mask
* frame
* frame_wait_cancel
* set_wiphy_netns
* set_channel
* probe_client
* set_noack_map
* register_beacons
* start_p2p_device
* set_mcast_rate
* connect
* disconnect
* channel_switch
* set_qos_map
* set_multicast_to_unicast
software interface modes (can always be added):
* AP/VLAN
* monitor
valid interface combinations:
* #{ AP } <= 8, #{ managed } <= 1,
total <= 8, #channels <= 1, STA/AP BI must match
HT Capability overrides:
* MCS: ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff
* maximum A-MSDU length
* supported channel width
* short GI for 40 MHz
* max A-MPDU length exponent
* min MPDU start spacing
Device supports TX status socket option.
Device supports HT-IBSS.
Device supports SAE with AUTHENTICATE command
Device supports scan flush.
Device supports AP scan.
Device supports per-vif TX power setting
Driver supports full state transitions for AP/GO clients
Driver supports a userspace MPM
Driver/device bandwidth changes during BSS lifetime (AP/GO mode)
Device supports static SMPS
Device supports configuring vdev MAC-addr on create.
max # scan plans: 1
max scan plan interval: -1
max scan plan iterations: 0
Supported TX frame types:
* IBSS: 0x00 0x10 0x20 0x30 0x40 0x50 0x60 0x70 0x80 0x90 0xa0 0xb0 0xc0 0xd0 0xe0 0xf0
* managed: 0x00 0x10 0x20 0x30 0x40 0x50 0x60 0x70 0x80 0x90 0xa0 0xb0 0xc0 0xd0 0xe0 0xf0
* AP: 0x00 0x10 0x20 0x30 0x40 0x50 0x60 0x70 0x80 0x90 0xa0 0xb0 0xc0 0xd0 0xe0 0xf0
* AP/VLAN: 0x00 0x10 0x20 0x30 0x40 0x50 0x60 0x70 0x80 0x90 0xa0 0xb0 0xc0 0xd0 0xe0 0xf0
* mesh point: 0x00 0x10 0x20 0x30 0x40 0x50 0x60 0x70 0x80 0x90 0xa0 0xb0 0xc0 0xd0 0xe0 0xf0
* P2P-client: 0x00 0x10 0x20 0x30 0x40 0x50 0x60 0x70 0x80 0x90 0xa0 0xb0 0xc0 0xd0 0xe0 0xf0
* P2P-GO: 0x00 0x10 0x20 0x30 0x40 0x50 0x60 0x70 0x80 0x90 0xa0 0xb0 0xc0 0xd0 0xe0 0xf0
* P2P-device: 0x00 0x10 0x20 0x30 0x40 0x50 0x60 0x70 0x80 0x90 0xa0 0xb0 0xc0 0xd0 0xe0 0xf0
Supported RX frame types:
* IBSS: 0x40 0xb0 0xc0 0xd0
* managed: 0x40 0xb0 0xd0
* AP: 0x00 0x20 0x40 0xa0 0xb0 0xc0 0xd0
* AP/VLAN: 0x00 0x20 0x40 0xa0 0xb0 0xc0 0xd0
* mesh point: 0xb0 0xc0 0xd0
* P2P-client: 0x40 0xd0
* P2P-GO: 0x00 0x20 0x40 0xa0 0xb0 0xc0 0xd0
* P2P-device: 0x40 0xd0
Maximum associated stations in AP mode: 128
Supported extended features:
* [ VHT_IBSS ]: VHT-IBSS
* [ RRM ]: RRM
* [ SET_SCAN_DWELL ]: scan dwell setting
* [ FILS_STA ]: STA FILS (Fast Initial Link Setup)
* [ CQM_RSSI_LIST ]: multiple CQM_RSSI_THOLD records
* [ CONTROL_PORT_OVER_NL80211 ]: control port over nl80211
* [ ACK_SIGNAL_SUPPORT ]: ack signal level support
* [ TXQS ]: FQ-CoDel-enabled intermediate TXQs
* [ AIRTIME_FAIRNESS ]: airtime fairness scheduling
* [ AQL ]: Airtime Queue Limits (AQL)
* [ CONTROL_PORT_NO_PREAUTH ]: disable pre-auth over nl80211 control port support
* [ SCAN_FREQ_KHZ ]: scan on kHz frequency support
* [ CONTROL_PORT_OVER_NL80211_TX_STATUS ]: tx status for nl80211 control port support
iw reg get
global
country PL: DFS-ETSI
(2400 - 2483 @ 40), (N/A, 20), (N/A)
(5150 - 5250 @ 80), (N/A, 23), (N/A), NO-OUTDOOR, AUTO-BW
(5250 - 5350 @ 80), (N/A, 20), (0 ms), NO-OUTDOOR, DFS, AUTO-BW
(5470 - 5725 @ 160), (N/A, 26), (0 ms), DFS
(5725 - 5875 @ 80), (N/A, 13), (N/A)
(5945 - 6425 @ 160), (N/A, 23), (N/A), NO-OUTDOOR
(57000 - 66000 @ 2160), (N/A, 40), (N/A)
phy#0
country PL: DFS-ETSI
(2400 - 2483 @ 40), (N/A, 20), (N/A)
(5150 - 5250 @ 80), (N/A, 23), (N/A), NO-OUTDOOR, AUTO-BW
(5250 - 5350 @ 80), (N/A, 20), (0 ms), NO-OUTDOOR, DFS, AUTO-BW
(5470 - 5725 @ 160), (N/A, 26), (0 ms), DFS
(5725 - 5875 @ 80), (N/A, 13), (N/A)
(5945 - 6425 @ 160), (N/A, 23), (N/A), NO-OUTDOOR
(57000 - 66000 @ 2160), (N/A, 40), (N/A)
Resources:
Provide regulatory.db info via /lib/firmware when supported
https://github.com/NixOS/nixpkgs/issues/57053
https://github.com/pcengines/apu2-documentation/issues/189#issuecomment-821185348
hostapd options (not sure who is more authorative)
https://github.com/usnistgov/hostap/blob/master/hostapd/hostapd.conf
Someone commented that w1.fi is more up to date
https://w1.fi/cgit/hostap/plain/hostapd/hostapd.conf
Wifi 5GHz AP Mode: What does no IR means and can I bypass it?
https://superuser.com/questions/809282/wifi-5ghz-ap-mode-what-does-no-ir-means-and-can-i-bypass-it
doc
https://wireless.wiki.kernel.org/en/users/documentation
https://wireless.wiki.kernel.org/en/users/drivers/ath10k/configuration
https://wireless.wiki.kernel.org/en/users/documentation/acs
https://wiki.gentoo.org/wiki/Hostapd
blogs
http://pisarenko.net/blog/2015/02/01/beginners-guide-to-802-dot-11ac-setup/
https://blog.fraggod.net/2017/04/27/wifi-hostapd-configuration-for-80211ac-networks.html
https://github.com/usableprivacy/upribox/issues/147
https://forums.raspberrypi.com/viewtopic.php?t=230168#p1559753
I followed this guide to add NFS to the NixOS config.
There is hope that hostapd will fully support ath10k soon.
https://github.com/NixOS/nixpkgs/pull/239780
Ps. I found an easier way to debug/play with your hostapd settings was to copy your hostapd.conf file over to your directory and then change the settings locally.
To find the location of the config file you can run this command:
systemctl status hostapd | more
● hostapd.service - hostapd wireless AP
Loaded: loaded (/etc/systemd/system/hostapd.service; enabled; preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Thu 2023-06-15 06:55:13 EDT; 1 week 4 days ago
Main PID: 899 (hostapd)
IP: 0B in, 0B out
IO: 6.9M read, 952.0K written
Tasks: 1 (limit: 4674)
Memory: 1.9M
CPU: 1h 9min 2.658s
CGroup: /system.slice/hostapd.service
└─899 /nix/store/frvw3b898rs8ra2728brj609vw5xdbg7-hostapd-2.10/bin/hostapd
/nix/store/8lzl1fx3r1p7hxfrhqghwyg3sdbzkphb-hostapd.conf
You need to stop hostapd:
systemctl stop hostapd
Then you can run hostapd with your local copy:
hostapd -dd hostapd.conf
nixos nfs
I migrated from FreeBSD to NixOS for my nas. Apparently I never tested/used NFS on the new OS. When I went to mount my music share from my OpenBSD client I received the following error.
NFS Portmap: RPC: Program not registered
I followed this guide to add NFS to the NixOS config.
That partially worked. I could use the local client in the example to connect and an Arch Linux client could connect. But my OpenBSD client would not connect.
After some (ok a lot) of searching I stumbled upon this guide, which suggested to run the below rpcinfo commands.
rpcinfo -t hostname mountd
rpcinfo -u hostname mountd
rpcinfo -t hostname nfs
rpcinfo -u hostname nfs
When I got to this one it became obvious what was really going on.
rpcinfo -u nas nfs
rpcinfo: RPC: Program not registered
program 100003 is not available
It turns out that OpenBSD defaults to using UDP for NFS and Linux defaults to TCP. When I had ran my rpcinfo command I didn’t notice that there was a UDP entry missing for the NFS service.
rpcinfo -p nas
program vers proto port
100000 4 tcp 111 portmapper
100000 3 tcp 111 portmapper
100000 2 tcp 111 portmapper
100000 4 udp 111 portmapper
100000 3 udp 111 portmapper
100000 2 udp 111 portmapper
100024 1 udp 4000 status
100024 1 tcp 4000 status
100005 1 udp 4002 mountd
100005 1 tcp 4002 mountd
100005 2 udp 4002 mountd
100005 2 tcp 4002 mountd
100005 3 udp 4002 mountd
100005 3 tcp 4002 mountd
100003 3 tcp 2049 nfs
100003 4 tcp 2049 nfs
100227 3 tcp 2049
100021 1 udp 4001 nlockmgr
100021 3 udp 4001 nlockmgr
100021 4 udp 4001 nlockmgr
100021 1 tcp 4001 nlockmgr
100021 3 tcp 4001 nlockmgr
100021 4 tcp 4001 nlockmgr
showmount -e nas
Exports list on nas:
export 192.168.88.0/24
export/music 192.168.88.0/24
I tried mount_nfs with the -T option to specify using TCP and it worked!
mount_nfs -T nas:/export/music /mnt/nas-media
I then hunted around for the flag for NixOS to add a UDP service for NFS. You need to add udp=y. The below is the NFS config for my NixOS.
services = {
nfs = {
server.enable = true;
server.exports = ''
/export 192.168.88.0/24(rw,fsid=0,no_subtree_check)
/export/music 192.168.88.0/24(rw,nohide,insecure,no_subtree_check)
'';
# for nvsv3
# fixed rpc.statd port; for firewall
server.statdPort = 4000;
server.lockdPort = 4001;
server.mountdPort = 4002;
server.extraNfsdConfig = ''udp=y'';
}:
}:
# Open ports in the firewall.
networking.firewall.enable = true;
networking.firewall.allowedTCPPorts = [ 111 2049 4000 4001 4002 20048 ];
networking.firewall.allowedUDPPorts = [ 111 2049 4000 4001 4002 20048 ];
Now rpcinfo shows:
rpcinfo -p nas
program vers proto port
100000 4 tcp 111 portmapper
100000 3 tcp 111 portmapper
100000 2 tcp 111 portmapper
100000 4 udp 111 portmapper
100000 3 udp 111 portmapper
100000 2 udp 111 portmapper
100005 1 udp 4002 mountd
100005 1 tcp 4002 mountd
100005 2 udp 4002 mountd
100005 2 tcp 4002 mountd
100005 3 udp 4002 mountd
100005 3 tcp 4002 mountd
100024 1 udp 4000 status
100024 1 tcp 4000 status
100003 3 tcp 2049 nfs
100003 4 tcp 2049 nfs
100227 3 tcp 2049
100003 3 udp 2049 nfs
100227 3 udp 2049
100021 1 udp 4001 nlockmgr
100021 3 udp 4001 nlockmgr
100021 4 udp 4001 nlockmgr
100021 1 tcp 4001 nlockmgr
100021 3 tcp 4001 nlockmgr
100021 4 tcp 4001 nlockmgr
Also NixOS supports NFS versions 3 through 4.2 and OpenBSD supports versions 2 and 3. However both OSs do successfully negotiate to use version 3.
offlineimap nametrans
I wanted to add a second email provider and have it integrated into my current Maildir folder so I didn’t have to jump through hoops configuring notmuch, emacs, and neomutt to use different Maildir directories.
The offlineimap nametrans doc hints at that but at least for me wasn’t clear enough on how to set that up.
In a new local repository section I added:
nametrans = lambda foldername: re.sub('\.gandi$', '', foldername)
And in a new remote repository section I added:
nametrans = lambda foldername: re.sub('(^INBOX|^Sent)', foldername + '.gandi', foldername)
folderfilter = lambda foldername: re.search('^INBOX$', foldername) \
or re.search('^Sent$', foldername)
The remote nametrans adds a suffix to my INBOX and Sent folders so they won’t collide with my other mail provider. The local one removes the suffix so it can be mapped back to my new provider.
The folderfilter restricts my download email to just those two folders.
Then in my first mail provider’s local repository section I added the below so offlineimap won’t try and sync the second providers folders to it:
folderfilter = lambda foldername: not re.search('\.gandi$', foldername)
You can find the scripts here
emacs/notmuch helper scripts part II
How to delete and move email - Part II
One of the ugly parts of doing a move this way was the helper shell script was hard coded and quite ugly. Each folder you wanted to support had to have an entry similar to the following:
notmuch search --format=text0 --output=files tag:move:inbox | xargs -n1 -0 -r -t ~/bin/my_mv.sh ~/Maildir/INBOX/cur/.
notmuch tag -move:inbox -flagged tag:move:inbox
I wrote a few elisp functions that pattern match your typed input with what folders exist in your Maildir directory and also allow for tab completion.
;; functions to move mail
;; in message move mail
(defun my-move-dir-msg-execute (&optional new-tags)
(notmuch-show-tag-message (concat "+move:" new-tags))
;;(rename-file (notmuch-show-get-filename) (concat "~/Maildir/" new-tags "/cur/"))
(notmuch-poll-and-refresh-this-buffer)
)
(defun my-move-dir-msg (&optional kill)
(interactive "P")
(let ((dirs (directory-files "~/Maildir" nil ))
(prompt (if kill "Copy DIR to kill ring: " "Browse DIR: "))
(fn (if kill #'kill-new 'my-move-dir-msg-execute)))
(if dirs
(funcall fn (completing-read prompt dirs nil nil nil nil (car dirs)))
(message "No DIRs found."))))
;; map for message
(define-key notmuch-show-mode-map "M" #'my-move-dir-msg)
;; in search view move message
(defun my-move-dir-search-execute (&optional new-tags)
;;(message "selected dir: %s" new-tags)
;;(message "move: %s" (concat "+move:" new-tags))
(notmuch-search-tag (list (concat "+move:" new-tags)))
(notmuch-poll-and-refresh-this-buffer)
)
(defun my-move-dir-search (&optional kill)
(interactive "P")
(let ((dirs (directory-files "~/Maildir" nil ))
(prompt (if kill "Copy DIR to kill ring: " "Browse DIR: "))
(fn (if kill #'kill-new 'my-move-dir-search-execute)))
(if dirs
(funcall fn (completing-read prompt dirs nil nil nil nil (car dirs)))
(message "No DIRs found."))))
Then I added the below snippet to my move shell script:
notmuch search tag:/move:.*/ | while read -r i
do
thread=`echo $i | cut -c1-23`
#dir=`echo $i | cut -c72- | cut -d':' -f2 | cut -d' ' -f1 | cut -d')' -f1`
dir=`echo $i | sed -e's/.*(.*move://' -e's/ .*)$//' -e's/)$//'`
echo 'thread: ' $thread 'dir: ' $dir
notmuch search --format=text0 --output=files tag:move:$dir | xargs -n1 -0 -r -t ~/bin/my_mv.sh ~/Maildir/$dir/cur/.
notmuch new >/dev/null 2>&1
notmuch tag -move:$dir -flagged -unread -- $thread
done
Now the move script has no hard coded folder names.
You can find the scripts here
FreeBSD ZFS umask issue
How to resolve not readable files
I am not sure how this started, but I assume I clicked some option on FreeNAS that set the ACL flag. Then I migrated to FreeBSD.
Unfortunately I set this flag on only a few directories and since I also had a hardware problem I didn’t notice right away or correlate it with other actions.
When I did discover it I was setting up a new NFS client to my NAS and thought it was an NFS issue.
Setting the ZFS ACL flag results in allowing you to create a file yet not being able to read it.
For example:
$ ls -l
total 1
---------- 1 jjf jjf 0 Nov 29 14:25 t
One way to tell if you have an ACL set is by the plus sign after the permissions.
drwxrwxr-x+ 14 jjf jjf 15 Nov 28 05:21 music
By running the following command you can recursively clear all ACLs that you may have set.
setfacl -Rb *
emacs/notmuch sent mail
How to copy an email to a sent folder
I have been puzzling over how to add my sent email to my Maildir/Sent folder. Clearly in FCC/BCC they describe the variable “notmuch-fcc-dirs” as a directory and in Maildir format.
However I could not get it to work. Since my mail provider handles plus addressing I decided to use that instead. I added a Bcc field to my header with my sent folder as a bcc in my init.el file.
(setq message-default-mail-headers "Bcc: mailID+Sent@mail.com")
Then after my Maildir sync program runs my Sent folder is copied down to my Maildir/Sent/cur directory.
emacs/notmuch helper scripts
How to delete and move email
Notmuch only indexes emails. They don’t modify any of your email in your Maildir folders.
This is mostly copied from other sites. However I am using OpenBSD and don’t have the GNU mv command with the -t flag to make life easy with the xargs command.
Edit: When I implemented emacs/notmuch helper scripts part II I had removed the “deleted” tag, since I wasn’t using it. By default notmuch will ignore any messages with this flag in a search. One thing I didn’t realize was this flag helps you visualize which messages are deleted in a thread with a lot of messages. I was just relying on the message residing in the Trash folder.
My emacs script now looks like:
(define-key notmuch-show-mode-map "d"
(lambda ()
"toggle deleted tag for message"
(interactive)
(if (member "move:trash" (notmuch-show-get-tags))
(notmuch-show-tag (list "-move:trash" "-deleted"))
(notmuch-show-tag (list "+move:trash" "+deleted" "-inbox" "-unread")))))
(define-key notmuch-search-mode-map "d"
(lambda ()
"toggle deleted tag for message"
(interactive)
(if (member "move:trash" (notmuch-search-get-tags))
(notmuch-search-tag (list "-move:trash" "-deleted"))
(notmuch-search-tag (list "+move:trash" "+deleted" "-inbox" "-unread")))))
My shell scripts look like:
notmuch_delete.sh:
/usr/local/bin/notmuch search --format=text0 --output=files "tag:deleted and not folder:Trash" | xargs -n1 -0 -r -t ~/bin/my_mv.sh ~/Maildir/Trash/cur/.
/usr/local/bin/notmuch new
my_mv.sh:
mv "$2" "$1"
Then after my Maildir sync program runs the message will be removed from the folder.
This can also be adopted to moving a message from one folder to another.
callerID
Finally cleaned up my caller ID blocker enough to publish it to git.
It uses a USRobotics USB modem to get the caller ID from a Plain Old telephone Service (POTS) line. It also announces the callers name from the address book via the connected speaker.
The repository is callerID
rssFeed
Finally cleaned up my news aggregator enough to publish it to git.
It will email you each story found in the news feeds. The repository is rssFeed
Welcome to my blog
This is a filler post. I hope to post about technical projects I am working on. These include IoT and general programming.
Test Post
This is a test post for mod date.
Testing image in sub-directory.
And an inline image following this: